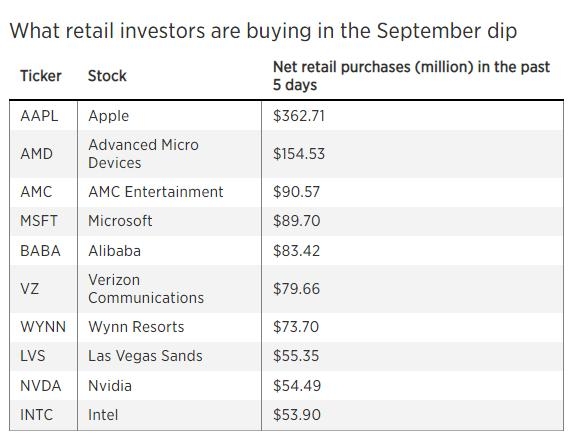
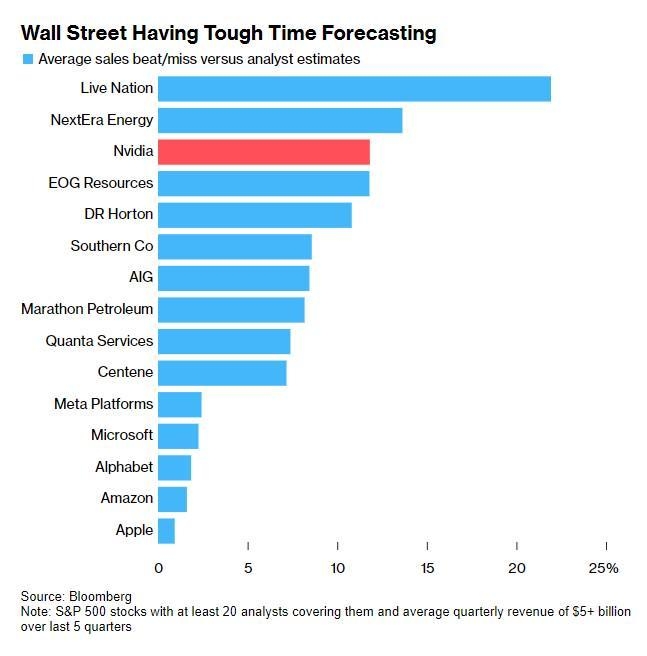
In the dynamic world of stock trading, margin requirements play a crucial role in determining how much leverage investors can use. For those unfamiliar with the term, "margin requirements" refer to the amount of money an investor must have in their account to borrow additional funds from a brokerage firm to purchase securities. This article delves into the ins and outs of US stock margin requirements, helping investors make informed decisions.
What Are US Stock Margin Requirements?
Margin requirements are set by the Federal Reserve and are designed to protect both the brokerage firm and the investor. The primary purpose of margin requirements is to ensure that investors have enough capital to cover potential losses if the value of the securities they have purchased on margin falls.
In the United States, margin requirements are governed by the Federal Reserve Board's Regulation T. Under this regulation, the initial margin requirement for stocks is typically set at 50%. This means that an investor must have at least 50% of the total value of the stock in their account to borrow the remaining 50% from the brokerage firm.
Understanding Margin Calls
One important aspect of margin requirements is the concept of a margin call. A margin call occurs when the value of the securities in an investor's account falls below the required margin level. When this happens, the brokerage firm may demand that the investor deposit additional funds to bring the account back up to the required margin level.
For example, if an investor has purchased
Risk and Reward
While margin trading can amplify gains, it also increases risk. Investors who use margin are exposed to margin calls, potential losses, and the risk of having their securities liquidated if they are unable to meet margin requirements.
It's important to note that margin requirements can vary depending on the type of security being traded. For example, the margin requirement for options is typically higher than for stocks, as options are more volatile and carry greater risk.
Case Study: Margin Calls in Action

Consider an investor who purchases
If the investor fails to meet the margin call, the brokerage firm may liquidate some or all of the securities in the account to cover the shortfall. This can result in significant losses for the investor, as the value of the securities may have fallen further since the initial purchase.
Conclusion
Understanding US stock margin requirements is essential for any investor looking to leverage their capital in the stock market. By knowing the rules and risks associated with margin trading, investors can make informed decisions and protect themselves from potential losses. Remember, while margin trading can amplify gains, it also increases risk, so it's important to trade responsibly and within your means.
railway stocks us
 railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....
railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....