In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, understanding the intricacies of the US bonds and stock market is crucial for investors looking to diversify their portfolios. This article delves into the dynamics of these two key investment vehicles, highlighting their unique characteristics and how they can impact your investment strategy.
What Are US Bonds?
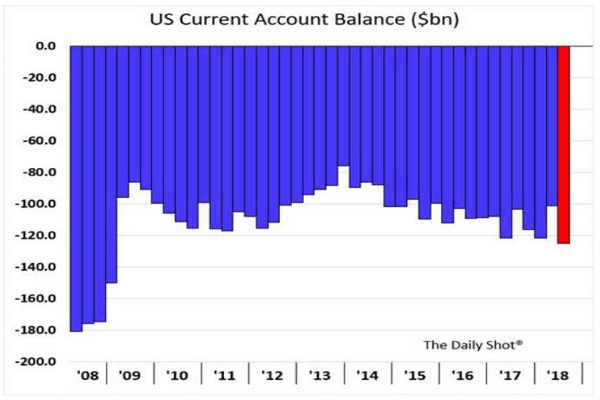
US bonds are debt securities issued by the United States government or corporations. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity. Government bonds, such as Treasury bonds, are considered to be among the safest investments due to the backing of the US government. Corporate bonds, on the other hand, are issued by companies and carry a higher level of risk compared to government bonds.
Understanding the Stock Market
The stock market is a marketplace where shares of publicly-traded companies are bought and sold. When you invest in stocks, you are purchasing a portion of the company's ownership. The value of your investment can fluctuate based on the company's performance and market conditions. The stock market offers investors the potential for high returns, but it also comes with higher risk compared to bonds.
The Relationship Between US Bonds and the Stock Market
The relationship between US bonds and the stock market is complex and interconnected. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Correlation and Volatility
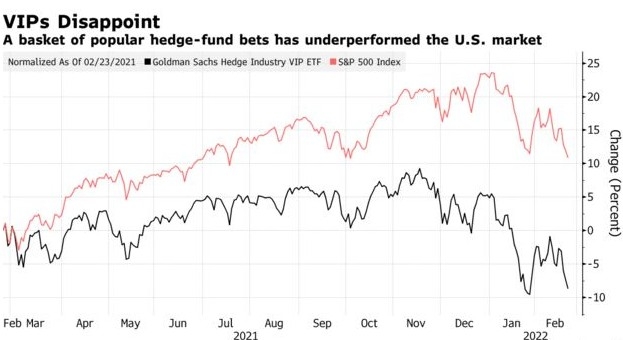
Historically, there has been a negative correlation between US bonds and the stock market. When the stock market is volatile or in a bear market, investors often seek the safety of bonds. Conversely, when the stock market is performing well, investors may move away from bonds in search of higher returns.
2. Yield and Interest Rates
Bonds offer fixed interest payments, known as yields, which are influenced by interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. This relationship can have a significant impact on the stock market, as investors may adjust their portfolios accordingly.
3. Market Sentiment
Market sentiment plays a crucial role in the dynamics between US bonds and the stock market. During periods of economic uncertainty or market stress, investors may seek the safety of bonds, leading to increased demand and higher prices. Conversely, during periods of economic growth and optimism, investors may be more inclined to invest in stocks.
Case Study: The 2008 Financial Crisis
One notable example of the relationship between US bonds and the stock market is the 2008 financial crisis. As the crisis unfolded, investors sold off stocks en masse, seeking the safety of bonds. This led to a significant increase in bond prices and a decrease in interest rates. Over time, as the economy began to recover, investors gradually moved back into the stock market, leading to a rebound in stock prices.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics between US bonds and the stock market is essential for investors looking to navigate the complex financial landscape. By considering factors such as correlation, yield, and market sentiment, investors can make informed decisions and build diversified portfolios that align with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
us stock market live
 railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....
railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....