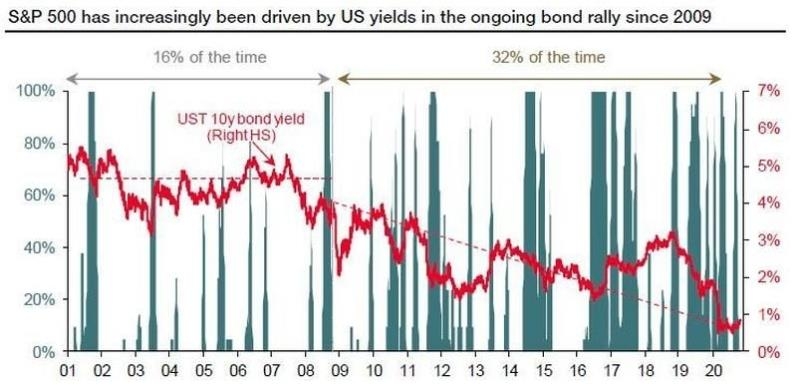
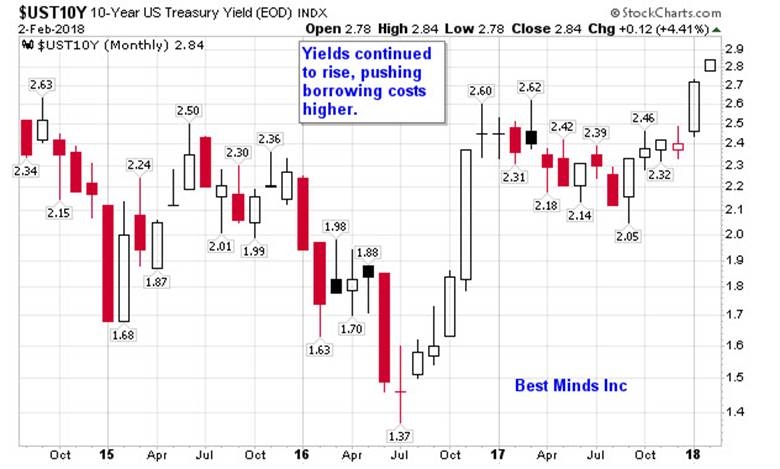
In the vast world of finance, the biggest US stock index is a beacon for investors and traders alike. This index, which represents the market capitalization of the largest and most influential companies in the United States, is a key indicator of the overall health and direction of the American economy. In this article, we will delve into the details of this crucial index, its history, components, and its impact on the financial markets.
Understanding the S&P 500
The S&P 500 is the most widely followed and recognized US stock index. It tracks the performance of 500 large companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. These companies are chosen based on their market capitalization, financial stability, and industry representation. The S&P 500 is a capitalization-weighted index, meaning that the weight of each company in the index is proportional to its market value.
History and Evolution
The S&P 500 was first introduced in 1957 by Standard & Poor's, a well-respected financial services company. Over the years, it has become the benchmark for measuring the performance of the US stock market. The index has evolved significantly, with companies being added or removed based on their market capitalization and other criteria.
Components of the S&P 500
The S&P 500 is composed of companies from various industries, including technology, healthcare, finance, consumer goods, and more. Some of the most prominent companies in the index include Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, and Google's parent company, Alphabet. The index is designed to represent a broad cross-section of the US economy, making it a valuable tool for investors looking to gain exposure to the American market.
Impact on the Financial Markets
The S&P 500 has a significant impact on the financial markets. Its performance is closely watched by investors, analysts, and policymakers. A rise in the index is typically seen as a positive sign for the economy, while a decline can indicate economic trouble ahead. The index is also used as a benchmark for mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and other investment vehicles.

Case Studies
One notable case study involving the S&P 500 is the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s. During this period, technology companies saw explosive growth, and their shares surged. The S&P 500, which included many of these companies, also experienced significant gains. However, when the bubble burst in 2000, the index plummeted, leading to widespread losses for investors.
Another example is the financial crisis of 2008. The S&P 500 fell sharply during this period, reflecting the turmoil in the global financial system. However, the index eventually recovered, demonstrating its resilience and ability to bounce back from significant downturns.
Conclusion
The biggest US stock index, the S&P 500, is a crucial indicator of the American economy and a valuable tool for investors. Its history, components, and impact on the financial markets make it an essential part of the financial landscape. By understanding the S&P 500, investors can gain valuable insights into the US stock market and make informed investment decisions.
new york stock exchange
 railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....
railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....