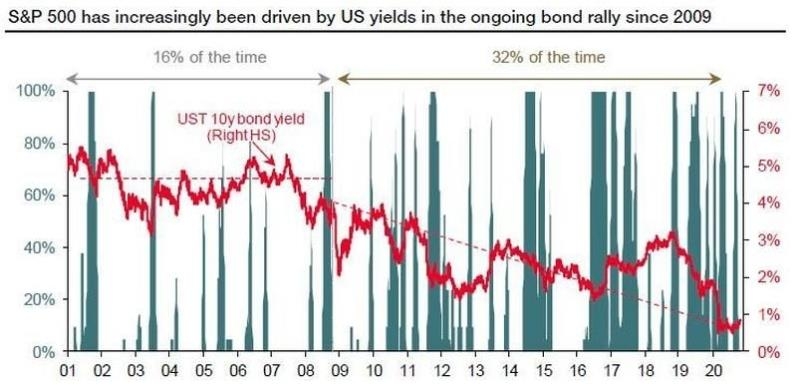
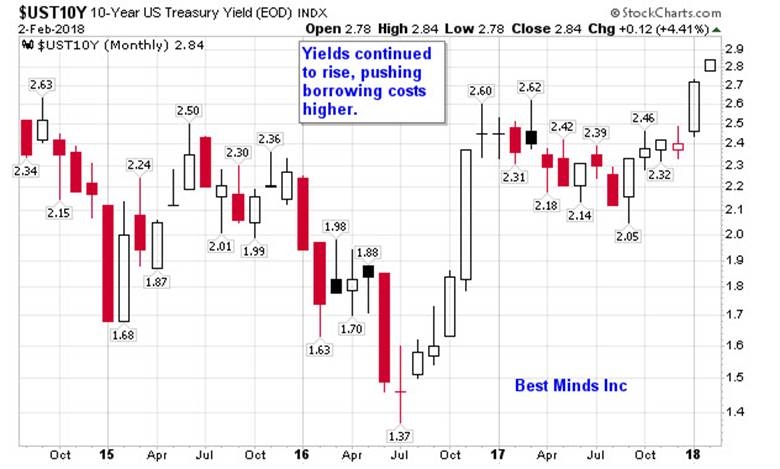
In the world of finance, the relationship between the US economy and the stock market is a topic that often sparks debate and intrigue. Understanding this relationship is crucial for investors, economists, and anyone interested in the financial landscape of the United States. This article delves into the dynamics of the US economy versus the stock market, highlighting key factors and providing insights into how they interact.
The US Economy
The US economy is the largest in the world, with a diverse range of industries and sectors. It is driven by factors such as consumer spending, business investment, government spending, and net exports. Economic indicators such as GDP, unemployment rate, and inflation are closely monitored to gauge the health of the economy.
The Stock Market
The stock market, on the other hand, is a reflection of the overall value of publicly traded companies. It is a barometer of investor sentiment and economic expectations. The S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, and NASDAQ Composite are some of the most well-known stock market indices in the United States.
The Relationship Between the US Economy and the Stock Market
The relationship between the US economy and the stock market is complex and multifaceted. Here are some key points to consider:
- Economic Growth: When the US economy is growing, businesses tend to perform well, leading to higher stock prices. Conversely, during economic downturns, businesses may struggle, leading to lower stock prices.
- Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve sets interest rates, which can have a significant impact on the stock market. Lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth and boost stock prices, while higher interest rates can slow down the economy and lead to lower stock prices.
- Inflation: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of money, leading to lower stock prices. However, moderate inflation can be a sign of a healthy economy.
- Investor Sentiment: The stock market is heavily influenced by investor sentiment. During periods of optimism, investors may be more willing to buy stocks, driving up prices. During periods of pessimism, investors may sell off their stocks, leading to lower prices.
Case Studies
One notable example of the relationship between the US economy and the stock market is the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s. During this period, the stock market experienced a significant boom, driven by the rise of the internet. However, this bubble eventually burst, leading to a sharp decline in stock prices and a subsequent recession.
Another example is the financial crisis of 2008. The stock market plummeted as the economy entered a severe recession, driven by factors such as the housing market collapse and the failure of major financial institutions.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between the US economy and the stock market is essential for anyone interested in the financial landscape of the United States. While the stock market can be influenced by a variety of factors, it is ultimately tied to the health of the economy. By keeping a close eye on economic indicators and investor sentiment, investors can better navigate the complexities of the stock market.
new york stock exchange
 railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....
railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....