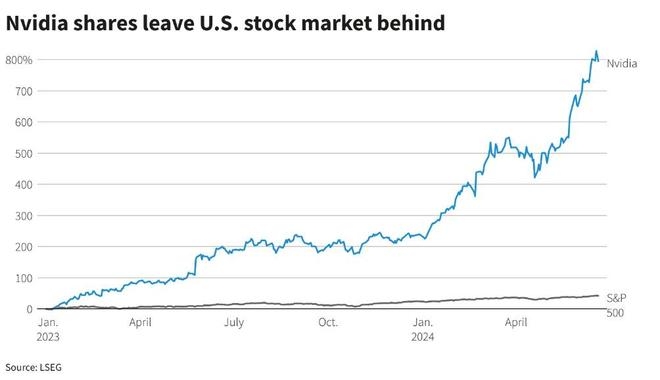
Are you considering selling gifted stock and want to understand the tax implications? This article delves into the intricacies of taxing gifted stock income in the United States. We'll explore the rules, potential tax liabilities, and provide real-life examples to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Gifted Stock
First, let's clarify what gifted stock is. Gifted stock refers to shares of a company that have been transferred to you as a gift from another individual. This could be from a family member, friend, or even a charity. Unlike inherited stock, gifted stock is subject to different tax rules.
Capital Gains Tax on Gifted Stock
When you sell gifted stock, the income generated from the sale is considered a capital gain. The tax rate on this gain depends on several factors, including your taxable income, the holding period of the stock, and the original cost basis of the gifted stock.
Original Cost Basis
The original cost basis of the gifted stock is crucial in determining the taxable gain. The cost basis is typically the price the original owner paid for the stock. When you sell the stock, the difference between the sale price and the cost basis is your capital gain.
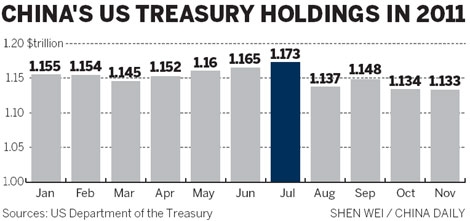
Holding Period
The holding period of the gifted stock also plays a significant role in determining the tax rate. If you hold the stock for more than a year, the gain is considered a long-term capital gain. This usually results in a lower tax rate compared to a short-term capital gain.
Tax Rate
The tax rate on long-term capital gains can vary depending on your taxable income. For example, if your taxable income is below
Real-Life Example
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario. John received 100 shares of Company XYZ as a gift from his uncle. The uncle purchased the shares for
Since John held the stock for more than a year, the gain is considered a long-term capital gain. Assuming John's taxable income is below $441,450, he will not owe any capital gains tax on the sale.
Potential Tax Liabilities
While the tax rate on gifted stock income is generally lower than other types of income, there are still potential tax liabilities to consider. These include:
- State Taxes: Some states tax capital gains, so it's essential to research your state's tax laws.
- Net Operating Loss (NOL) Deduction: If you have a net operating loss, you may be able to deduct some of your capital gains.
- Tax Planning: It's crucial to consult with a tax professional to ensure you're maximizing your tax benefits and minimizing your liabilities.
Conclusion
Selling gifted stock can be a lucrative investment strategy, but it's essential to understand the tax implications. By familiarizing yourself with the rules and potential liabilities, you can make informed decisions and optimize your tax situation. Remember to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice and guidance.
us stock market today live cha
 railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....
railway stocks us-Backed by SEC-compliant security protocols and 24/7 market support, we don’t just let you trade U.S. stocks—we empower you to invest with confidence, clarity, and a competitive edge that sets you apart.....